Molded Plastic Aspheres

- Available Uncoated or with an AR Coating for 400 - 700 nm or 650 - 1050 nm
- Ø3 mm or Ø6 mm
- Diffraction-Limited Design at 633 nm
APL0615-B
(Ø6 mm)
APL0303
(Ø3 mm)
APL0618
(Ø6 mm)
APL0606-A
(Ø6 mm)
APL0303-B
(Ø3 mm)

Please Wait
Click to Enlarge
Click for Raw Data
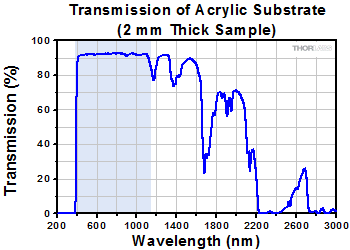
The shaded region represents the recommended wavelength range for the uncoated acrylic. This data was measured using a 2 mm thick sample.
| Click on the red Document icon next to the item numbers below to access the Zemax file download. Our entire Zemax Catalog is also available. |
Features
- Ø3 mm and Ø6 mm Sizes
- Focal Lengths Available from 3.00 mm to 24.00 mm
- Numerical Apertures Available from 0.10 to 0.38
- Available Uncoated or with an AR Coating for 400 - 700 nm or 650 - 1050 nm
- Substrate: Acrylic
- Excellent for use in OEM Applications
- Volume Pricing is Available by Contacting Technical Support
Aspheric lenses are designed to eliminate spherical aberration, which allows for the spot size and collimation of a monochromatic beam of light to approach the diffraction limit. The Molded Plastic Aspheric Lenses offered here are available uncoated or with an antireflection coating deposited on both sides for either the 400 - 700 nm or 650 - 1050 nm range. In addition, these aspheres are fabricated from acrylic, which is half as dense as N-BK7, making them ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
In laser diode systems, difficulties with aberration correction are compounded by the beam's high divergence angle. Since individual spherical lenses can refract light at only small angles before spherical aberration is introduced, three or four optical elements are often required to collimate laser diode light. In contrast, a single aspheric lens collimates without introducing spherical aberration. When used to collimate light, the lens should be oriented so that the side with a larger radius of curvature (i.e., the flatter surface) faces the point source.
Conversely, when coupling into fiber, it is often necessary to focus the laser light to a near-diffraction-limited spot. With single spherical elements, spherical aberration, rather than the diffraction limit, serves as the limiting factor to achieving a small spot size. The diffraction-limiting design of these aspheric lenses helps to minimize spherical aberration, allowing the focal spot size to approach the diffraction limit. For focusing applications, the lens should be oriented so that the side with a smaller radius of curvature (i.e., the more curved surface) faces the source.
To mount the Ø3 mm or Ø6 mm aspheres sold on this page, we recommend the LMR05(/M) fixed lens mount along with either the LMRA3 mounting adapter for Ø3 mm optics, or the LMRA6 mounting adapter for Ø6 mm optics.
Common Specifications
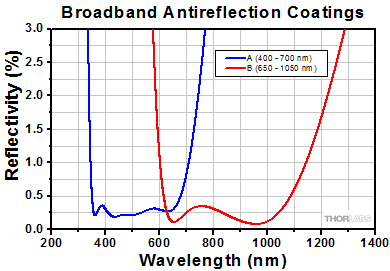
Please see the Graphs Tab for AR Coating Details
| Item # | APL0303a | APL0606a | APL0609a | APL0615a | APL0618a | APL0624a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer Diameter | 3.0 mm | 6.0 mm | 6.0 mm | 6.0 mm | 6.0 mm | 6.0 mm |
| Focal Length | 3.00 mm | 6.00 mm | 9.00 mm | 15.00 mm | 18.00 mm | 24.00 mm |
| Focal Length Shift (Raw Data) | ||||||
| NA | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.10 |
| Clear Aperture | Ø2.0 mm | Ø5.0 mm | Ø5.0 mm | Ø5.0 mm | Ø5.0 mm | Ø5.0 mm |
| Working Distance | 0.991 mm | 2.942 mm | 6.226 mm | 12.121 mm | 15.069 mm | 20.964 mm |
| Surface Quality | 60-40 Scratch-Dig | |||||
| Material | Acrylic | |||||
| Edge Thickness | 2.1 mm | 2.7 mm | 2.9 mm | 3.4 mm | 3.5 mm | 3.6 mm |
| Center Thickness | 3.0 mm | 4.5 mm | 4.0 mm | 4.0 mm | 4.0 mm | 4.0 mm |
| Design Wavelength | 633 nm | |||||
| RMS | Diffraction Limited at the Design Wavelength | |||||
| Spot Size | ||||||
| Operating Temperature | 10 to 85 °C | |||||
These high-performance multilayer AR coatings have an average reflectance of less than 0.5% (per surface) across the specified wavelength ranges and provide good performance for angles of incidence (AOI) between 0° and 30° (0.5 NA). For optics intended to be used at large incident angles, consider using a custom coating optimized at a 45° angle of incidence; this custom coating is effective from 25° to 52°. The plot shown below indicates the performance of the standard coatings in this family as a function of wavelength. Broadband coatings have a typical absorption of 0.25%, which is not shown in the reflectivity plots.

Click to Enlarge
Figure 2. Lens with a rough gate vestige along its entire length (left) and along part of its length (right).

Click to Enlarge
Figure 1. Lens with a flat gate vestige along its entire length (left) and along part of its length (right).
The appearance of these lenses is expected to vary slightly from unit to unit. Due to the degating process during manufacturing, some lenses possess a gate vestige that keeps their outer diameter from being fully round. The gate vestige can be a flat cut (see Figure 1) or a rough notch (see Figure 2), extending entirely or partly along the length of the lens.
The maximum cut of the gate vestige is specified as 0.38 mm into the lens diameter (click on the red Docs icon (![]() ) for more information). The gate vestige results in cosmetic differences and will not affect the specifications or performance of the lens.
) for more information). The gate vestige results in cosmetic differences and will not affect the specifications or performance of the lens.
| Posted Comments: | |
prathmesh ghag
(posted 2021-03-18 16:24:30.897) I am thinking of using this lens APL0303-A to focus a beam from a 5 mW HeNe laser (632.8nm).
The laser will be on for over 8 hours.
Since, this is a plastic component, do you think it will wear out due to the lasers power?
Will it get heated up and degrade its focus spot size?
Thank you for your time.
regards,
Prathmesh Ghag YLohia
(posted 2021-03-18 02:13:30.0) Hello Prathmesh, thank you for contacting Thorlabs. These lenses can be used up to an operating temperature of 65 C. We would not expect your low power CW HeNe laser to damage the optic in this case since your laser shouldn't put the lens temperature over the 65 C spec (under normal conditions). parksj003
(posted 2019-02-27 21:39:21.017) Hello,
We are interested in plastic lens with various temperature. I have few queations in you product.
1. I am wondering that how do you define the operating and storage temperatures?
2. For some products, the operating and storage temperatures are different, even though their plastic materials are the same. Would you let me know why?
3. What happen to the plastic lens if we increase temperature up to 140 °C.
4. With high temperature, which one is more durable between coated plastic lens and uncoated one.
Seongjun Park nbayconich
(posted 2019-04-05 10:48:13.0) Thank you for contacting Thorlabs.
1)The max operating temperature for these plastic lenses is defined as the max temperature the optics can be used before the material becomes soft or looses shape, we specify a value of 65 degrees max as a safe value however the optic can be technically used up to the storage temperature of 80 degrees Celsius before becoming deformed. We will update the web specifications as soon as possible.
2)The materials of the APL vs the CAY series asperes are both acrylic however the bulk material of the arylic is from different vendors. We suggest using them within the parameters specified on our webpage as the bulk material we receive from our vendors may vary slightly.
3)The acrylic material will not be able to withstand temperatures up to 140 degrees celsius unfortunately, they can only be used at 80 degrees celsius Max for the APL series plastic aspheres.
4)The uncoated lenses will have the same maximum operating temperatures as the coated lenses, as the temperature limit is determined by the plastic material. werner.engel
(posted 2018-12-09 12:57:36.78) I'm missing the Right mount for the lenses like APL0606. In finding the right one I was so unsure that I selected a speric one. They have mounting Options allready included. YLohia
(posted 2018-12-14 11:53:06.0) Hello, thank you for your feedback. For the APL0606-B, we recommend the LMRA6 adapter to be used with the LMR05 mount. We will improve the visibility of the appropriate mounts on this page. boruiche
(posted 2015-01-19 10:57:45.91) For 532nm wavelength, what is the maximum input power for this acrylic lens can work? ie, thermal expansion will happen above specific power. besembeson
(posted 2015-01-27 01:25:44.0) Response from Bweh at Thorlabs USA: We don't have damage threshold specifications for these polymer lenses yet. I will contact you by email for your full laser specifications to suggest whether these might be suitable for your application. tobias.kuhlen
(posted 2014-04-29 11:52:29.06) What is the focal shift for this lens for 450 nm? jlow
(posted 2014-04-29 02:04:29.0) Response from Jeremy at Thorlabs: The focal length shift for APL0606 at 450nm is estimated to be around -110.2µm. |
 Products Home
Products Home










 Plastic Aspheres 60-40 Scratch-Dig
Plastic Aspheres 60-40 Scratch-Dig